Describe the Cell Membrane and Its Properties
Describe the fluid properties of the cell membrane and vesicles. The cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell.
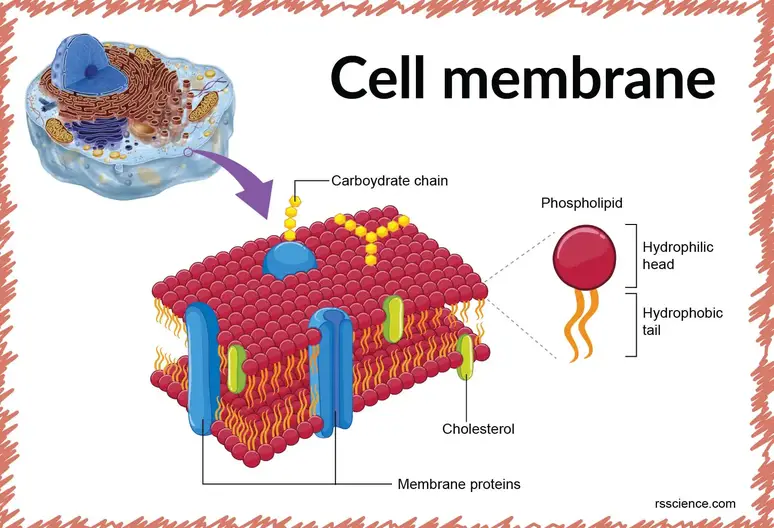
Cell Membrane Definition Structure Function And Biology
The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cells cytoplasm.
. The cell membrane surrounds all cells. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. THE CELL MEMBRANE AND ITS PROPERTIES 3 say or imply that there is a barrier to free diffusion at least of some sub stances between the cell and the medium surrounding it that this barrier is situated at the cell surface and that it is a special structure called the cell membrane.
Thin barrier separating inside of cell cytoplasm from outside environment Function. Transmembrane transport proteins - peripheral proteins bound to surface of membrane. A morphological delimitates the cell from its external microenvironment and confines all of its subcellular organelles.
1 Isolate cells contents from outside environment 2 Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3 Communicate with other cells Note. All cells have a fluid but defining cell membrane that encircles the cytoplasm a cell membrane provides a barrier to separate the cytoplasm from the extracellular space. Composition of the cell membrane.
Vesicles move materials within cells. All cells have a plasma membrane which encloses the cell and allows interactions between the cell and its environment The plasma membrane has three functions 1 Isolates the cells internal contents from the external environment 2 Regulates the flow of materials into and out of the cell 3 Allows communication with other cells. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a thin closed sheet that fulfils a double role. Lipids 50 by weight Outer membrane. Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane.
Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals. We describe here the results of a study on the relative contributions to toxicity of the physicochemical properties of protein. Impermeable to water-soluble molecules but not to water Soft and flexible.
Distinguish neighboring cells from one another-integral proteins penetrate into lipid bilayer. Na binding is associated with phosphorylation generates a membrane potential rate-limited by intracellular Na. Structure and Composition of the Cell Membrane.
14U2 The fluidity of membranes allows materials to be taken into cells by endocytosis or released by exocytosis. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cells shape. This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out.
-The cell membrane pinches off to form an extracellular vesicle joined to the cell by filaments-The cell membrane invaginates and pinches off creating a vesicle within the cell-The cell selectively filters small nutrients through specialized membrane pores-The cell synthesizes proteins that pump large hydrophilic materials into the cell. B functional regulates the exchange of substance between internal and external media maintains actively the ionic asymmetry between its sides and intermediates. The cell membrane regulates the transport of.
Na-K ATPase Ca2 ATPase H-K ATPase transports 3 Na out of and 2 K into cells inhibitied by cardiac glycosides composed of 2 α 95 kd binds ATP and digoxin and 2 ß 40 kd glycoprotein subunits. Physical properties of the cell membrane. Explain vesicle formation via endocytosis.
The cell membrane also called the plasma membrane is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. Spontaneously prone to forming self-repairing pores. Outline two examples of materials brought into the cell via endocytosis.
Each lipid molecule has a hydrophilic phosphorylated head and a hydrophobic fatty acid tail. It separates the cytoplasm the contents of the cell from the external environment. The fundamental unit of all biological life is the cell a mass of biomolecules in watery solution surrounded by a cell membraneOne of the characteristic features of a living cell is that it controls the exchange of electrically charged ions across the cell membrane and therefore the electrical potential of its interior relative to the exterior.
The hydrophobic parts of the molecules on the bilayer face each other whereas the hydrophilic parts form the inner and outer surfaces of the cell membrane. The plasma membrane also known as the cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of a cell from its outside environment. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane.
Recognition proteins glycoproteins cell identity. These cells are eukaryotic and have internal compartments called membrane-bound organelles. Membranes also exist within cells forming various.
Key role in cell-cell recognition. A 3D diagram of the cell membrane. It is a feature of all cells both prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
-carbohydrates are hydrophilic and stick out of cell membrane. A cell membranes structure and properties like having hydrophilic outer areas and hydrophobic inner regions prevents many substances from entering or leaving a cell. Increasing evidence suggests that the interaction of misfolded protein oligomers with cell membranes is a primary event resulting in the cytotoxicity associated with many protein-misfolding diseases including neurodegenerative disorders.
The exact mix or ratio of proteins and lipids can vary depending on the function of a specific cell. Just as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment the cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. The cell membrane is a fluid matrix made of a phospholipid bilayer.
As the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment the cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. Things are brought in and things are shipped out of all cells but it would be dangerous to let just anything pass through them. Not much inside it is static or stationary including the cell membrane that surrounds it.
The primary function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out. The cell membrane eg.
In plant cells the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. However some cells have internal cell membranes as well.
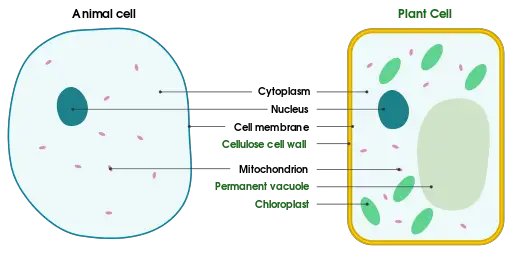
Cell Membrane Definition Function Structure Animal Plant Cell
Do Plant Cells Have A Cell Membrane Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Membrane Definition Structure Functions Britannica

Cell Membrane The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
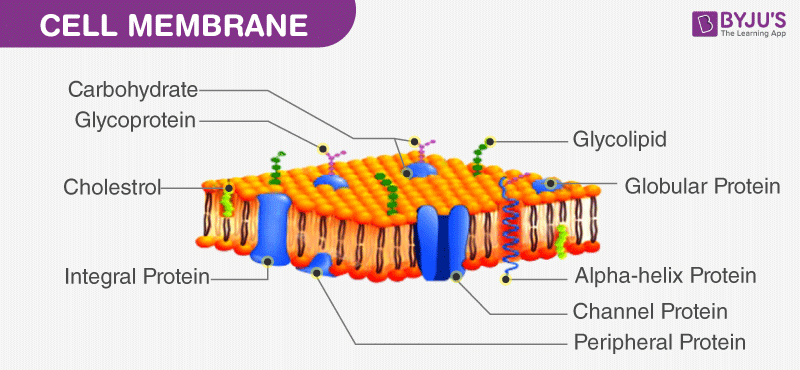
Cell Wall And Cell Membrane Structure Functions And Differences
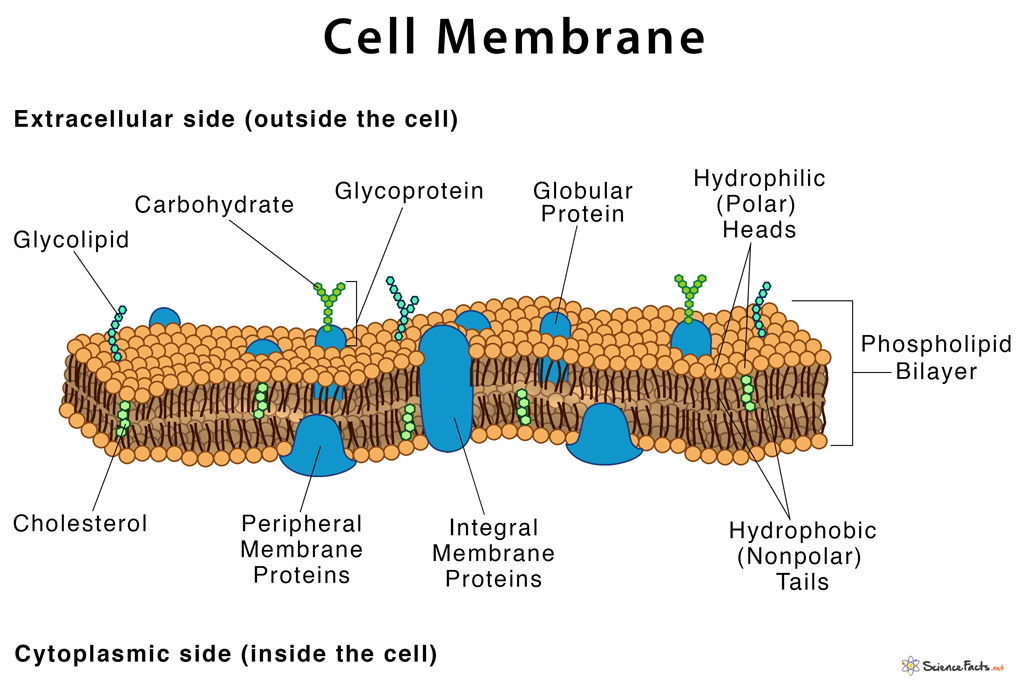
Cell Membrane Definition Structure Functions With Diagram
Composition And Properties Of Cell Membranes Deranged Physiology

Membranes Anatomy And Physiology I

Fluid Mosaic Model Cell Membranes Article Article Khan Academy
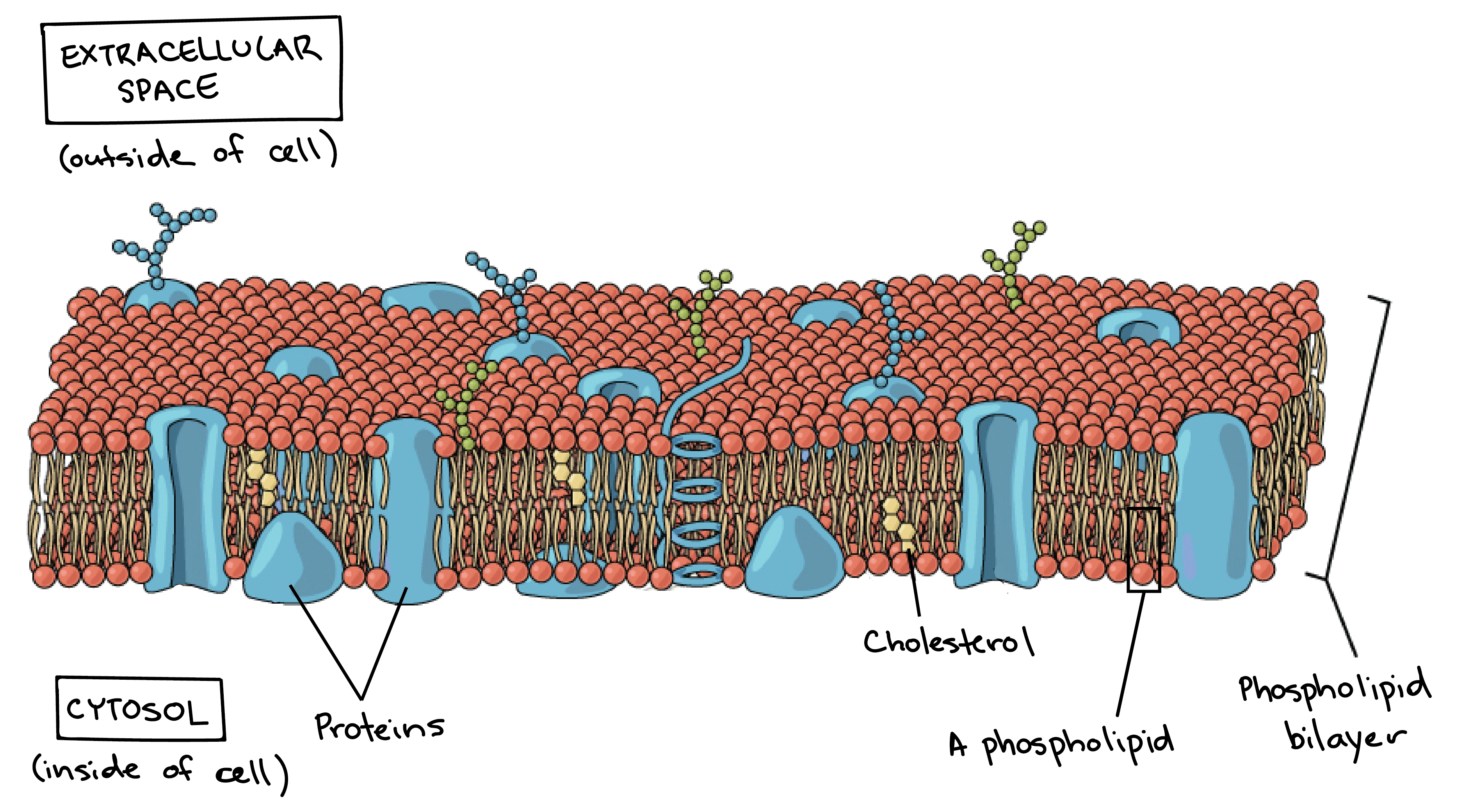
Plasma Membrane And Cytoplasm Article Khan Academy
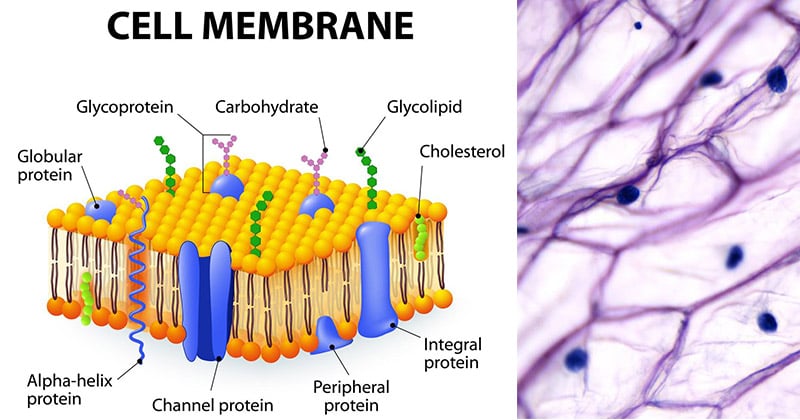
Cell Plasma Membrane Structure Composition Functions

Plasma Membrane Or Cell Membrane Structure And Function Qs Study

Plasma Membrane Definition Structure Functions Biology Dictionary

Membrane Definition Structure Functions Britannica
Cell Membrane Structure Of The Cell

Cell Membrane Structure And Function Biology Wise

Biology Diagram Show Structure Of Cell Membrane Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
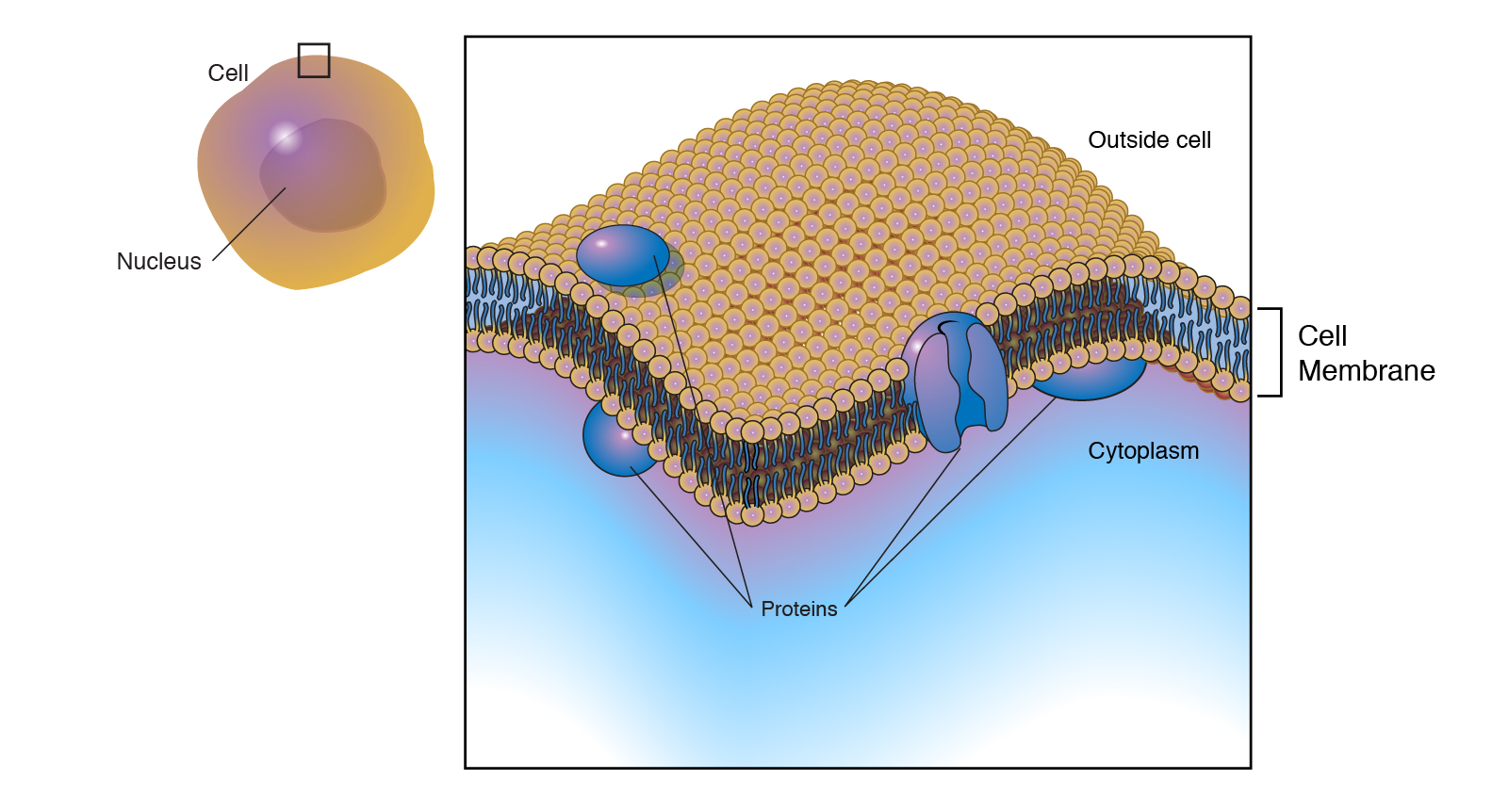
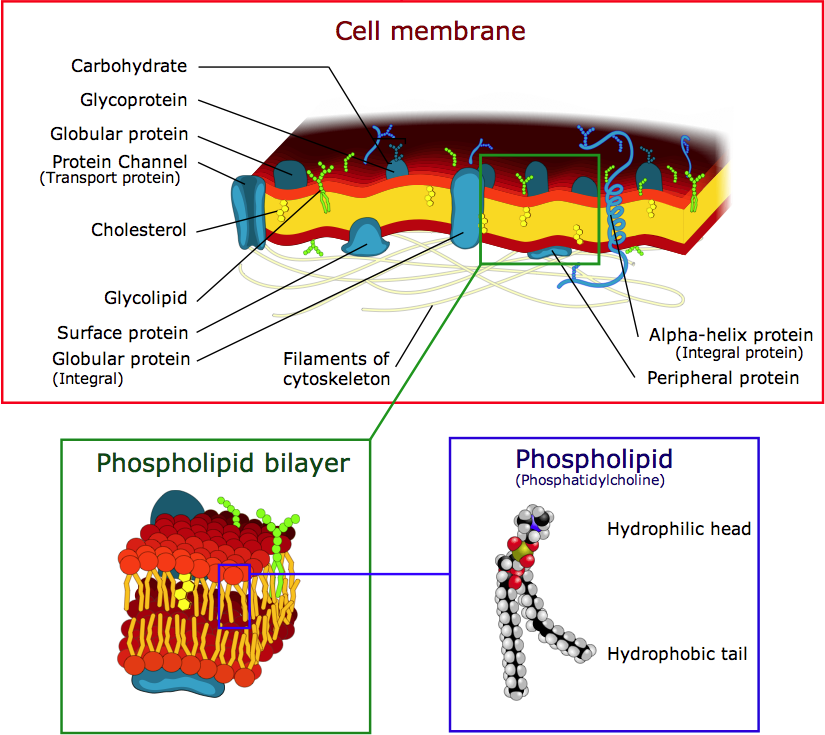
Comments
Post a Comment